
How does it work? (cont)
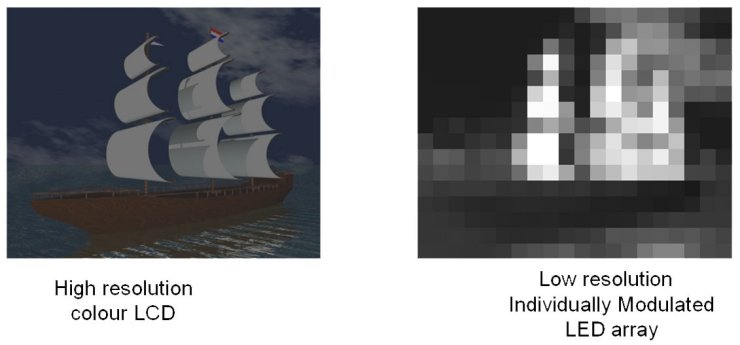
We left off scratching our head has to how a 45x31 array of LEDs could possibly modulate the luminance of over 2 million pixels on our 1920x1080 high definition LCD TV.The LEDs are arranged in an array where the luminance of each LED can be individually controlled faster than video refresh rates. This LED back light array effectively constitutes a low-resolution, but very high brightness display. This low-resolution white-light LED image is then projected through a standard colour LCD panel, which displays a similar, but high resolution, version of the image.
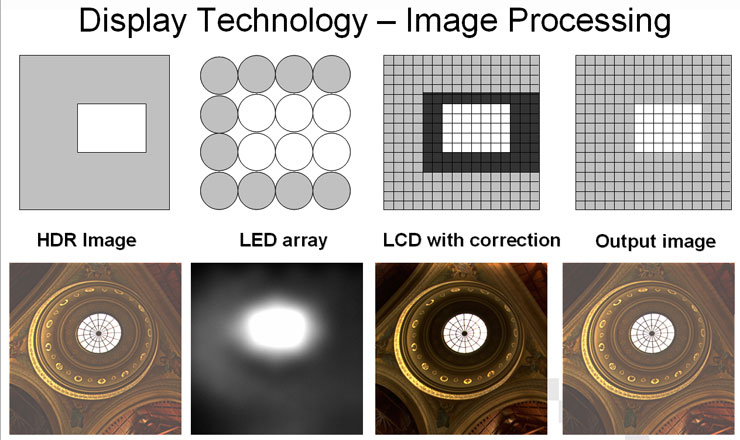
Each individually controlled LED back lights a small region of the LCD panel. This has the effect of multiplying the modulation of the two displays which provides the substantial gain in dynamic range. The patented BrightSide 'special sauce' is a set of software image algorithms that take into account the natural effects of scattered light in the human eye. This natural effect, called veiling luminance, is the effect you get when looking at a bright light on a dark background and get a blur or bloom caused by the scattering of light.
Game developers try to simulate this HDR effect by simulating bloom and effect in the images. In the BrightSide HDR display, the LCD pixels are recalculated to compensate for this and the result is a high resolution, high dynamic range final image.


MSI MPG Velox 100R Chassis Review
October 14 2021 | 15:04








Want to comment? Please log in.